Braitenberg Vehicle
In this assignment you will create a controller which navigates a turtlebot robot through an obstacle course. The steps to complete this task will be outlined but the exact code/commands needed you will have to figure out yourself using what you have learned in the lecture, the information available on this website or what you can find on the internet.
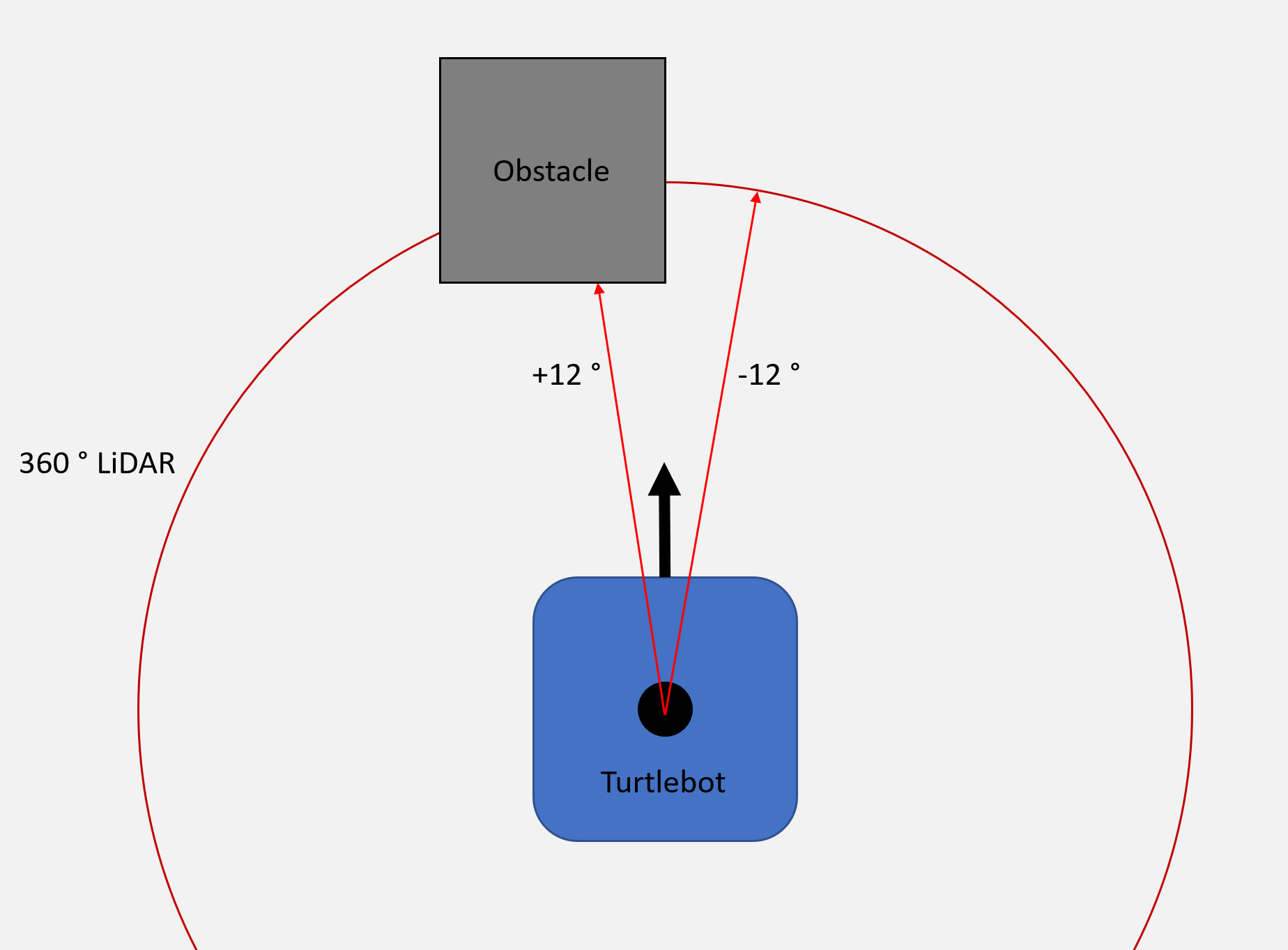
You will control a Turtlebot in a simulated environment. Using two points (+12 and -12 degrees) from the 360 degree onboard LiDAR as input, the robot should show the following behaviours:
- No obstacles are detected -> move forward
- Only the left sensor detects an obstacle -> turn right
- Only the right sensor detects an obstacle -> turn left
- Both sensors detect an obstacle -> stop
Setup Process
- Open a new terminal by pressing: Ctrl+Alt+T
- Change directory into the source folder of your ROS2 workspace:
cd ~/ros2_ws/src - Create a ROS2 python package with the name braitenberg_vehicle:
ros2 pkg create --build-type ament_python braitenberg_vehicle - Copy the folders launch, urdf and worlds from the ros2_students_25/braitenberg_vehicle git repository to your newly created package (ros2_ws/src/braitenberg_vehicle)
- In ROS2 the python scripts of packages are located in a folder with the same name as the package. Copy the file controller.py from the ros2_students_25/braitenberg_vehicle git repository to the scripts folder of your package (ros2_ws/src/braitenberg_vehicle/braitenberg_vehicle)
- In the setup.py file of your package add the following lines:
# Add after: from setuptools import setup import os from glob import glob # In order to be able to access the added files during runtime we add we add them to data_files # Add after: ('share/' + package_name, ['package.xml']), (os.path.join('share', package_name, 'launch'), glob(os.path.join('launch', '*.launch.py'))), (os.path.join('share', package_name, 'worlds'), glob(os.path.join('worlds', '*.world'))), (os.path.join('share', package_name, 'urdf'), glob(os.path.join('urdf', '*.xacro'))), #To make our python script excecutable with ros2 run, we add a entry_points definition #Add after: 'console_scripts': [ 'controller = braitenberg_vehicle.controller:main', - Move to workspace directory, build your workspace and source it:
cd ~/ros2_ws colcon build --symlink-install source install/setup.bash - To launch the simulation use:
ros2 launch braitenberg_vehicle spawn_robot.launch.py - To run the controller script use:
ros2 run braitenberg_vehicle controller
Assignment Steps
- Open up the controller.py file with the editor of you choice (e.g. Visual Studio Code). Inside the python script you will find comments showing you where to write the different code snippets (marked with TODO).
- Figure out what meessage types your publisher and subscriber topics have and import them.
- Initialize a ros node.
- Create a subscriber to the /scan topic using as a callback function the already existing function inside the class called clbk_laser.
- Create a publisher to the /cmd_vel topic.
- Inside the timer_callback function set vel_msg.linear.x and vel_msg.angular.z depending on the values from self.lidar_left_front and self.lidar_right_front as described in the introduction of this assignment.