Wall Follower and Go-To-Point
This assignment is the first part of two to create a Bug2 algorithm for navigating a Turtlebot to a target destination. The goal for the overall exercise is for you to be able to implement a navigation algorithm and learn to use the different communication patterns available in ROS2. The assignments are split as follows:
- Implement a wall follower and a go-to-point controller which use ROS topics for communicating with the robot.
- Implement a bug2 controller which uses the already established wall follower and go-to-point controllers. The bug2 controller should enable and disable the wall follower and go-to-point controllers using their ROS services. For sending a target location to the bug2 controller an action server should be created.
In this assignment both the Wall Follower as well as the Go-To-Point algorithm uses the /cmd_vel topic to control the movement of the robot. You should already be familiar with using it from the first assignment.
Wall Follower
The Wall Follower basically has 3 modes:
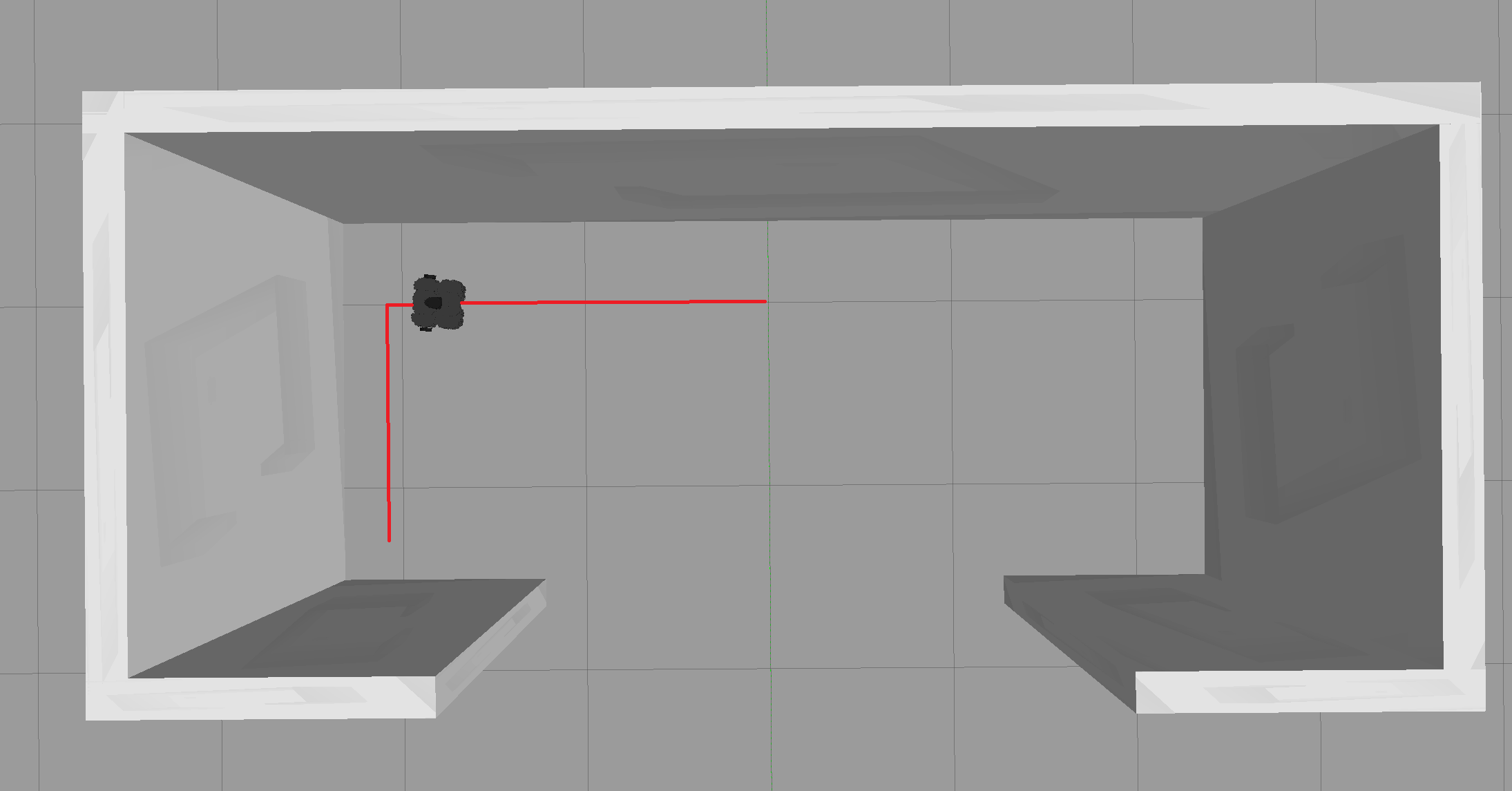
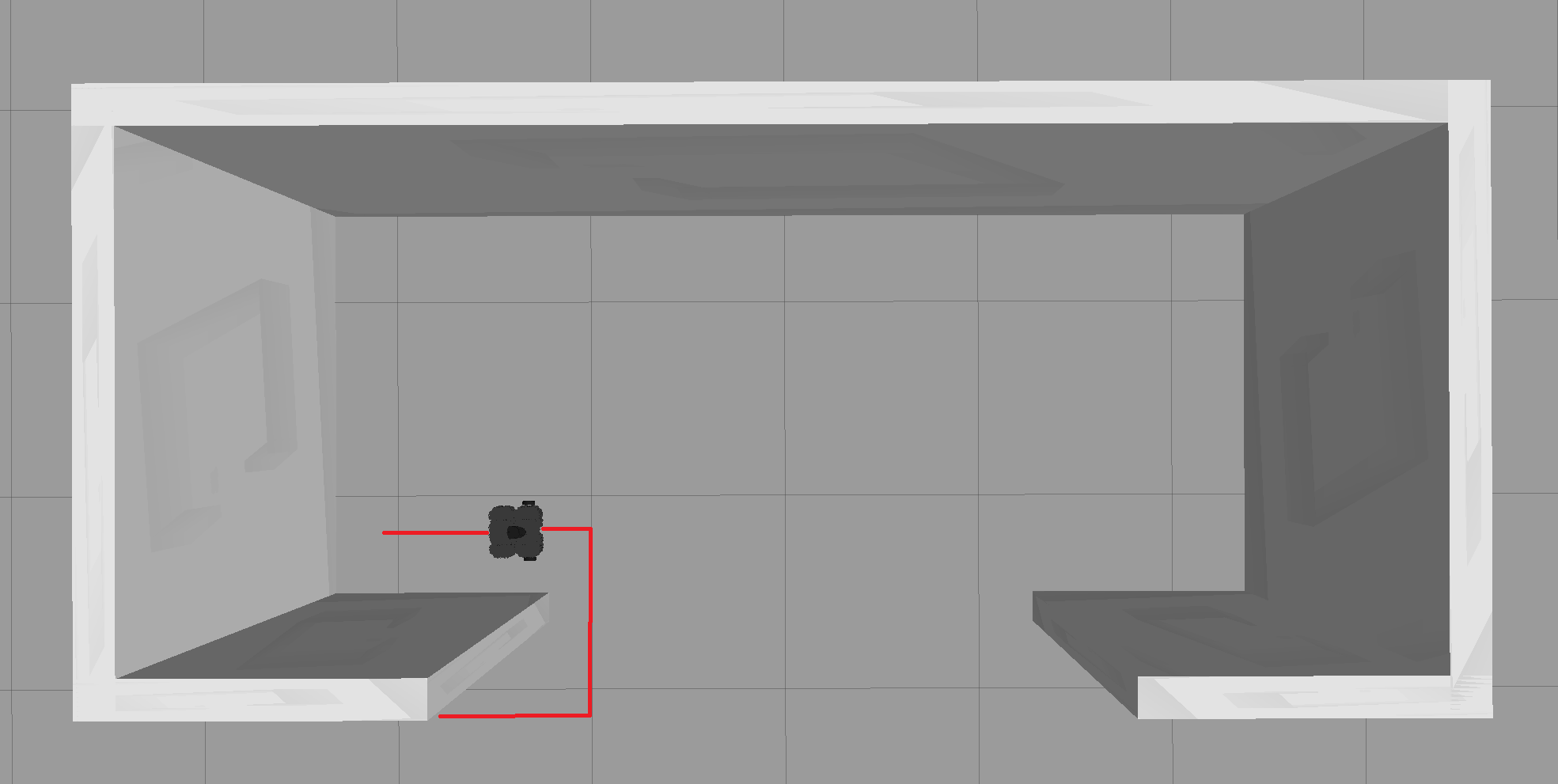
- When next to a wall drive parallel to it using the LiDAR sensor topic (/scan) to ensure the robot is not straying off
- When a wall appears in front of the robot the robot has to reorient itself before going back to mode 1:
- A special case you will also need to take care of is when the wall suddenly stops you need to program a behavior which moves the robot to where the wall continues:
Go-To-Point
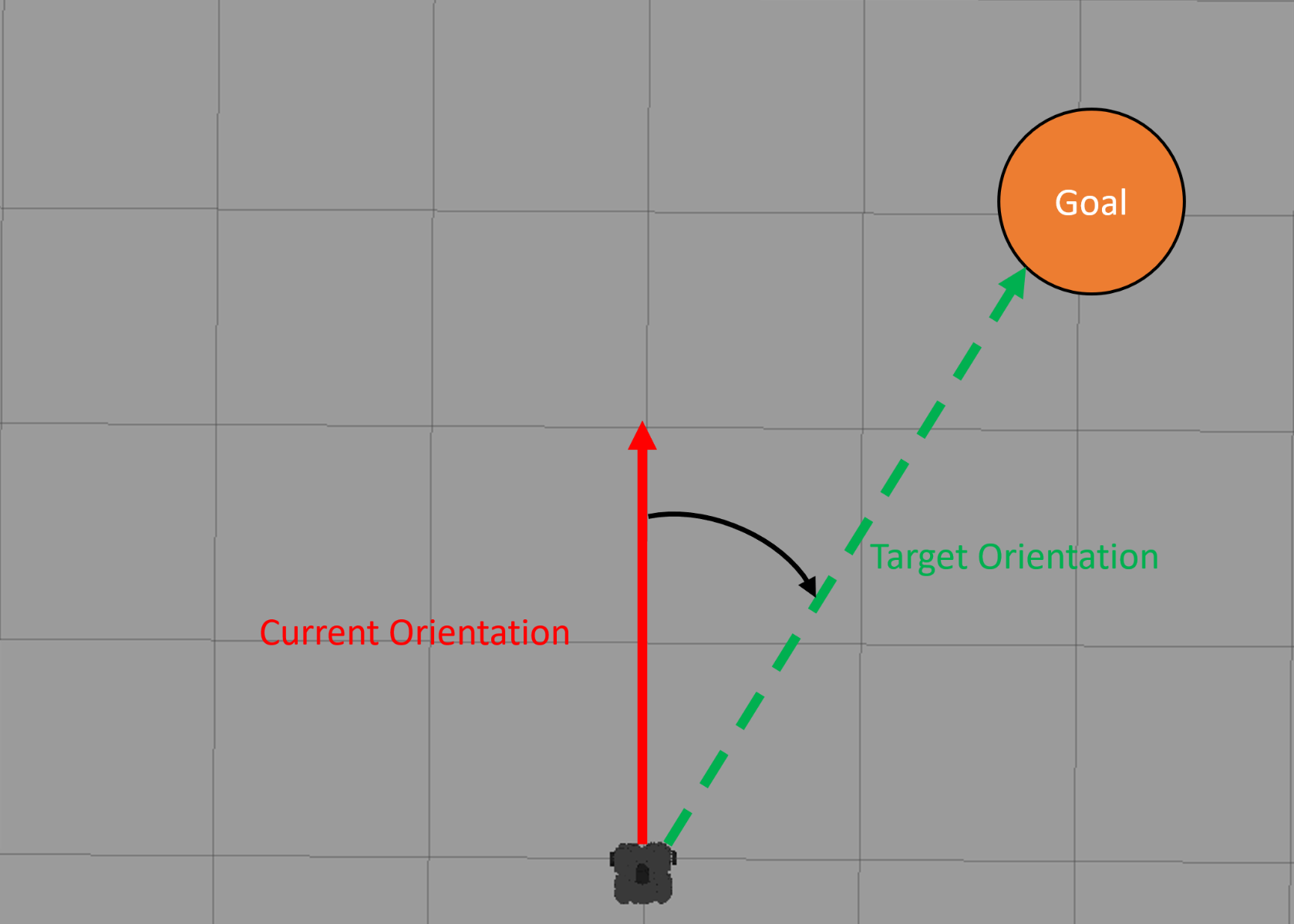
The go-to-point algorithm takes as input a target position. It then turns the robot until it faces that target and starts moving forward. While moving straight the controller needs to make sure that the robot doesn’t stray off by constantly correcting the direction if necessary. To get the position and orientation of the robot subscribe to the odometry sensor topic (/odom). The orientation is given in quaternions which is a mathematical number system used to describe orientations in a 3D space. Since it is out of the scope of this course to explain how it works you can use the following callback function for the odometry topic which extracts the position (self.position) of the robot and the orientation around the z axis (self.yaw).
from tf_transformations import euler_from_quaternion
def clbk_odom(self, msg):
self.position = msg.pose.pose.position
quaternion = (
msg.pose.pose.orientation.x,
msg.pose.pose.orientation.y,
msg.pose.pose.orientation.z,
msg.pose.pose.orientation.w)
euler = euler_from_quaternion(quaternion)
self.yaw = euler[2]
Setup Process
For setting up the assignment follow these steps:
- Create a ROS2 python package with the name bug2_navigation
- Copy the folders launch, rviz and worlds from the ros2_students_25/bug2_navigation git repository to your newly created package.
- Don’t forget to adjust your setup.py file so that it copies the files from the previously copied folder into the install folder during colcon build. Look at braitenberg_vehicle assignment on how to do that.
- Add any script you make under ‘console_scripts’ in your setup.py file. This allows you to use ros2 run to start the script. For this assignment you will need one script for the wall follower algorithm and one for the go-to-point algorithm. The syntax for adding scripts in the setup.py file is as follows:
#Add after: 'console_scripts': [ 'ROS_RUN_NAME = PACKAGE_NAME.SCRIPT_NAME:main', - To launch the simulation environment use:
ros2 launch bug2_navigation spawn_robot.launch.py - To run your control scripts after you made them and added them to setup.py use the following syntax:
ros2 run PACKAGE_NAME ROS_RUN_NAME